SEO(Search Engine Optimization) is the most important marketing platform in today’s AI era. The Global Search Marketing Software market is set to rise from USD 3.76 billion in 2024 to USD 4.22 billion in 2025, a year‑over‑year increase of 12.3 percent. I discuss what search engine optimization is, how it impacts digital marketing, and how it works, types, sectors, history, tools, career opportunities, and a lot of other things.
What is SEO?
SEO stands for (search engine optimization). The Optimization/Refinement of websites to show in search engines to gain traffic. In a more complex or detailed definition, search engine optimization is the set of ongoing practices/improvements where search engines they easily found, crawled, and indexed. SEO helps more people find your website, whether you’re selling products, offering services, or sharing expert information.

Today, Top Search engines include Google, Bing, Yandex, Yahoo, etc.
Search Engine | Global Market Share (%) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
Google | 89.5% – 89.7% | Dominant worldwide, slight decline from past years |
Bing | 3.98% – 4.0% | Second largest globally; strong presence in U.S. with AI integration |
Yandex | 2.5% – 2.6% | Leading search engine in Russia and nearby regions |
Yahoo! | 1.3% – 1.4% | Powered by Bing; notable in Japan and some markets |
DuckDuckGo | 0.79% – 0.82% | Privacy-focused; growing slowly worldwide |
Baidu | 0.6% – 0.7% | Dominant in China with over 50% market share there; low global share due to regional focus |
What is SEO in Digital Marketing?
SEO in digital marketing is a type of marketing where you gain non-paid traffic from organic search results. Unlike the ads, which is temporarily give you traffic, and when the ads is off the traffic is also goes to 0 but in seo websites takes to rank and gain traffic but it consistent and long-term also its unpaid.. 53.3% Average website traffic from organic search Compared to only 5% from social media. 748% (or $7.48 return per $1 spent) Average ROI from SEO delivers one of the highest ROI among digital marketing channels.
What is AEO in SEO?
AEO in SEO in 2025 is now the most important need. As SEO is the search engine optimization, the AEO is the answer engine optimization like ChatGPT, prexipility AI search engine, etc..
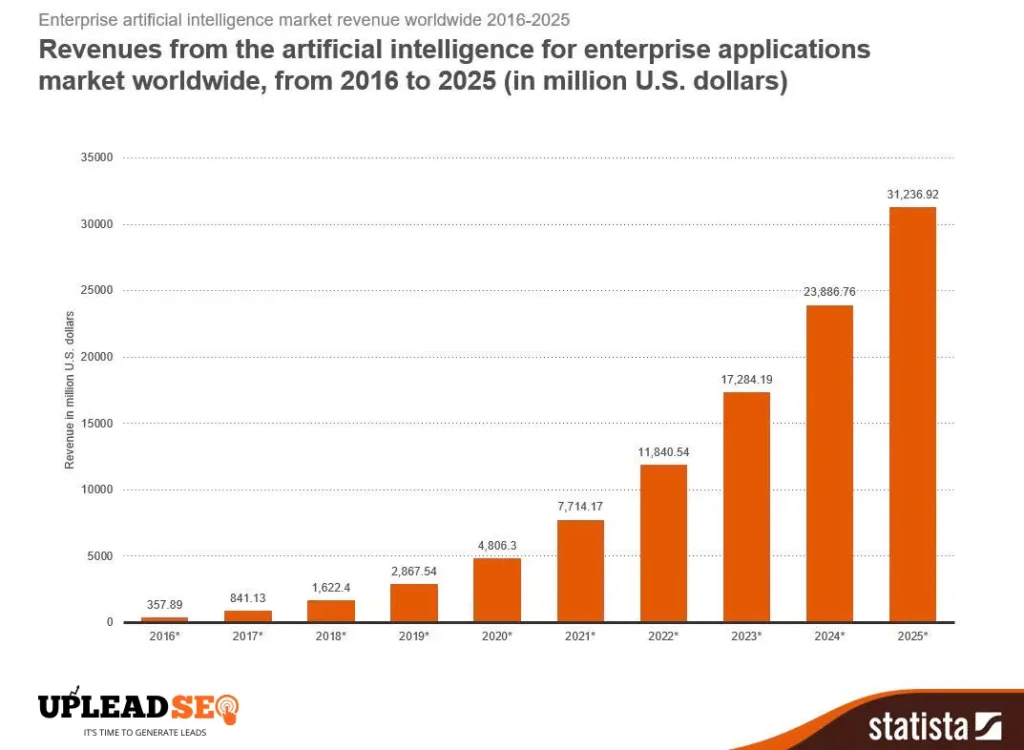
The global AI search engine market is projected to grow from USD 43.63 billion in 2025 to USD 108.88 billion by 2032, at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 14.1%.
How Seo Works?
Search Engine Optimization works start with crawling, indexing, and serving, then ranking. Search engines have very complex algorithms to understand the content of the websites and assign a score to it! Search engines like Google have indexed 50 billion web pages, which is a very large number. Google has 14,000 ranking factors that apply to websites and decide their rankings.
A Step by step-by-step process is like search engines’ crawlers regularly crawl the web, collecting, organizing web pages.
# | Stage | What Happens |
|---|---|---|
1 | Crawling | Googlebot discovers new or updated pages by following links, reading XML sitemaps, and using URL submission APIs. |
2 | Indexing | The crawler’s snapshots are parsed & stored in Google’s distributed index (≈ 50 billion pages, per your paragraph). Duplicate content is removed, key entities and structured data are extracted. |
3 | Serving | When a user enters a query, Google’s front‑end fetches candidate pages from the index that might satisfy search intent, matching on text, entities, freshness, location, etc. |
4 | Ranking | A multilayer ranking pipeline applies signals—page quality, link graph, user behavior, Core Web Vitals, and more (≈ 14 000 factors, per your paragraph)—to assign scores and order results before they are returned in < 1 s. |
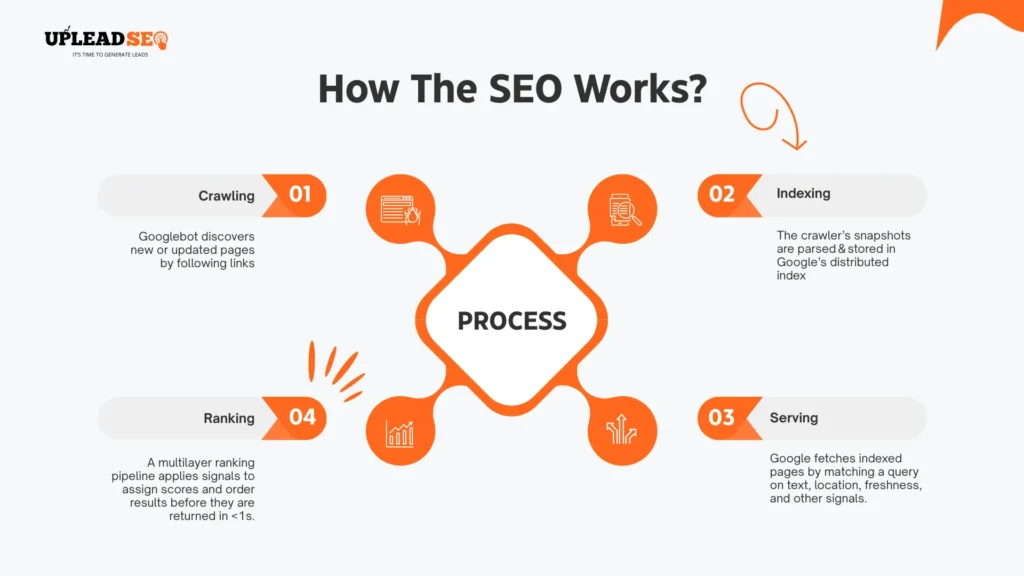
Note: Google does not fetch every time from their index; they already have cached SERPs to show users for every possible query.
Why SEO Matters?
SEO matters because it’s every business’s need. How? 8.3 billion searches per day on Google. It’s an organic marketing strategy to take organic traffic and convert it into organic leads rather than paid ads. Seo matters because SEO is cost-effective compared to paid advertising. 54 % of all clicks go to the top three organic results on page 1. In 2025, where Artificial Intelligence search era seo is most important for businesses. 53 % of website traffic is driven by organic search.
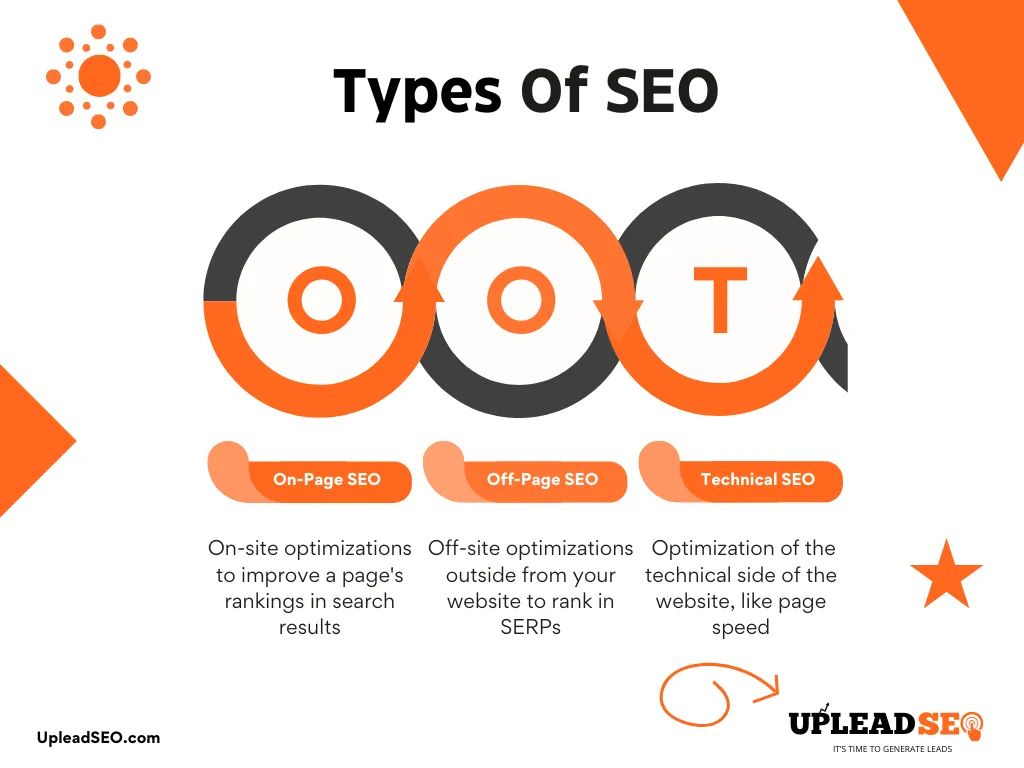
What are the Types Of SEO?
Types of SEO include On-page, Off-page, and Technical SEO. Semantic SEO is not a type but a whole emerging method to do optimization of search engines. Local SEO is a subtype of seo. Image & video SEO is also an important aspect of seo.
On-page SEO
On-page seo, also called On-site seo, with its name telling the seo what we do on-page, like meta-description, heading tags, image metadata, video, content configuration, internal linking, etc..
Off-page SEO
Off-page or off-site seo when you do seo other than on your site, but for your website. What does it mean? Earn links from outside websites—and from other pages within your own site—to channel authority to the page you’re optimizing. Backlinks and a solid reputation are the off-page MVPs.
Technical SEO
Technical SEO is the optimization of the technical side of the website, like page speed, JavaScript minify, unused CSS, mobile mobile-responsive UI.
Local SEO
Local SEO is the seo where we optimize businesses or websites for their local location. For example, if a website is in New York, we optimize for seo to rank on the New York Google SERP to visit their local audience.
Semantic SEO
Semantic seo means when you do optimization of websites without worrying about keyword difficulty, density, or volume. It’s SEO when you understand the meaning behind the seo rather than just a list of keywords. It’s a complete framework of optimizing websites using today’s search engine algorithm strategies rather than old 2012 strategies.
How Many Sectors Can SEO Be Applied To?
SEO benefits every sector. Here are some noted industries:
E-commerce SEO:
E-commerce SEO covers every technical and on-page element that helps your store rank and convert, including
- Strategic optimization of category and product pages
- clean, hierarchical product URL architecture
- structured data, internal linking, and performance tuning
Partner with our(upleadseo) agency to put these proven, data-driven tactics to work and turn search traffic into measurable revenue growth.
Enterprise SEO:
Enterprise SEO involves optimizing large, complex websites with millions of pages, aligning organic search visibility with enterprise-level business goals. It also relies on automation and a large-scale approach.
International SEO
International SEO is the practice of optimizing a website to rank well in search engines across multiple countries and languages. It involves a combination of a lot of practices 3 are technical adjustments, content localization, and language translation.
News SEO
This seo is a totally new-oriented SEO that focuses specifically on getting time-sensitive journalism to surface in Google News, the “Top Stories” carousel, Google Discover, Microsoft Start, Apple News, and other news-oriented search features. The primary goal is to make news articles easily discoverable by both search engines and readers as soon as they’re published.
SEO for lawyers
SEO for lawyers (or “legal”) is used to gain visibility online for a law firm’s website and online content to rank higher in search engine results for relevant legal queries, such as “divorce lawyer near me”.
Automotive SEO
Automotive SEO is the seo for the automotive industries its the mix of local-search, inventory, and content optimizations that help every segment of the auto industry—dealerships, repair shops, parts retailers, rental agencies—show up when shoppers Google queries like “used Hyundai IONIQ 5 near me” or “brake repair open today.” The goal? Greater visibility, more organic traffic, and increased leads or sales.
Healthcare SEO
The healthcare industry is the most sensitive industry in the eyes of Google and generally also. Because health advice is deeply Y-M-Y-L (“Your Money or Your Life”), Google applies extra scrutiny: only pages that radiate E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trust) and respect patient privacy win sustained visibility.
Dental SEO
Dental SEO (search engine optimization for dentists) is enhancing the online presence on search engines to attract more customers for a dental clinic. According to the SOCi Consumer Behavior Index 2024, 80% of US consumers search online for local businesses on a weekly basis, and 32% do so daily. In this era, Clinics need to have online visibility to attract customers.
Real Estate SEO
Real-Estate seo is helps brokerages, agents, and property portals surface when buyers and renters Google things like “2-bed flat in New York” or “best real estate agent near me.” The goal? to generate leads online on how to do SEO for a real estate business.
Educational SEO
Educational SEO is the SEO of schools, colleges, universities, MOOC platforms, bootcamps, and tutoring centres to make online visibility in search engines that leads to generating leads.
History of Search Engines!
The idea of an automated information retrieval system predates the World Wide Web. In 1945, Vannevar Bush, an American engineer and science administrator, envisioned a device he called the “memex” in his seminal essay “As We May Think.” The memex was a hypothetical electromechanical device that would allow individuals to store, organize, and retrieve vast amounts of information, creating associative trails between related documents—a concept remarkably similar to modern hyperlinks.
The true genesis of search engines coincided with the dawn of the Internet. Before the widespread adoption of the World Wide Web in December 1990, early Internet search tools focused on indexing files and users within nascent network environments. The WHOIS user search, dating back to 1982, and the Knowbot Information Service (KIS), implemented in 1989, were among the first multi-network user search systems.
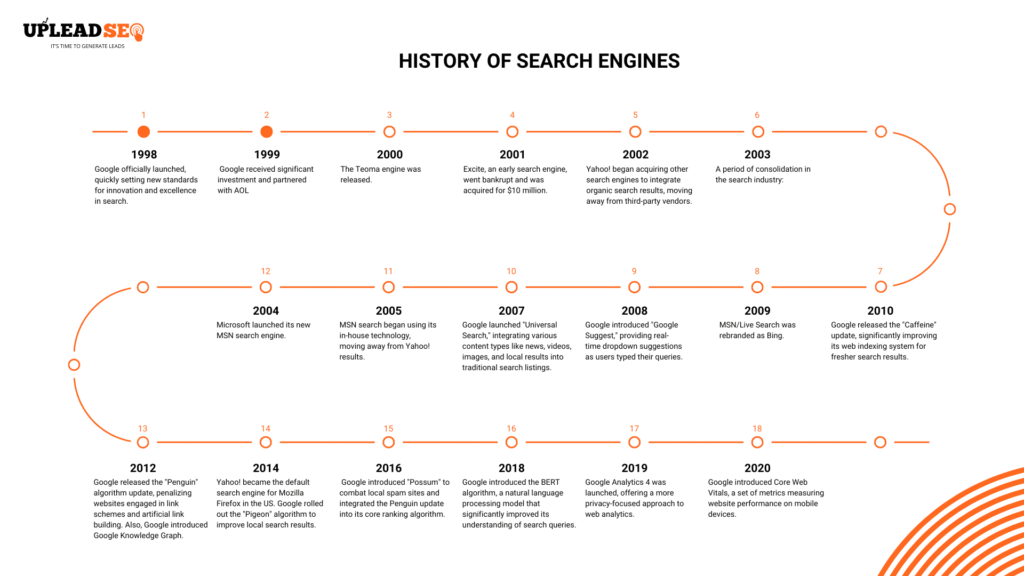
Archie (1990)
The first well-documented search engine was Archie, created in 1990 by Alan Emtage, a computer science student at McGill University in Montreal. Archie’s primary function was to index File Transfer Protocol (FTP) sites, allowing users to search for specific files.
It achieved this by periodically downloading directory listings from public anonymous FTP servers and building a searchable database of file names. However, Archie did not index the content within these files, meaning users needed to know the exact file name they were looking for. Despite this limitation, Archie represented a significant step towards automated information discovery on the Internet.
The Google Era and Modern Search (Late 1990s – Present)
1998– Google officially launched, quickly setting new standards for innovation and excellence in search.
Overture (formerly Goto.com): This company successfully implemented a PPC model, demonstrating the viability of paid search advertising.
1999– Google received significant investment and partnered with AOL, further solidifying its position.
2000– The Teoma engine was released.
2001– Excite, an early search engine, went bankrupt and was acquired for $10 million. Ask Jeeves to adopt Teoma to replace its direct search engine.
2002– Yahoo! began acquiring other search engines to integrate organic search results, moving away from third-party vendors.
2003– A period of consolidation in the search industry:
AllTheWeb acquired Overture for $70 million.
Yahoo! purchased Inktomi for 235 million and subsequently acquired Overture for 235 million and subsequently acquired Overture for 235 million and subsequently acquired Overture for 1.63 billion.
Google introduced its first significant search algorithm update, known as the “Boston” update.
2004– Microsoft launched its new MSN search engine.
2005– MSN search began using its in-house technology, moving away from Yahoo! results. IAC acquired Ask Jeeves for $1.85 billion, rebranding it as Ask.com and discontinuing the Teoma platform. Major search engines introduced the “nofollow” tag to combat spam in blogs.
2007– Google launched “Universal Search,” integrating various content types like news, videos, images, and local results into traditional search listings.
2008– Google introduced “Google Suggest,” providing real-time dropdown suggestions as users typed their queries.
2009– MSN/Live Search was rebranded as Bing.
2010– Google released the “Caffeine” update, significantly improving its web indexing system for fresher search results. Google Instant provided real-time search results as users typed.
2011– Google, Yahoo!, and Microsoft collaborated to create Schema.org, aiming for a more structured internet. Google launched the “Panda” algorithm update, targeting content farms and scraper sites and affecting 12% of all US search results.
2012– Google released the “Penguin” algorithm update, penalizing websites engaged in link schemes and artificial link building. Also, Google introduced the Google Knowledge Graph.
2013– Google introduced the “Hummingbird” update, a major overhaul designed to better understand the human intent behind search queries, moving beyond keyword matching.
2014– Yahoo! became the default search engine for Mozilla Firefox in the US. Google rolled out the “Pigeon” algorithm to improve local search results. Google also emphasized website security as a ranking factor with its HTTPS Everywhere campaign.
2015– Google launched “Mobilegeddon,” an update that prioritized mobile-friendly websites in search rankings, acknowledging the surge in mobile search. Google also released RankBrain, a machine-learning program that automates parts of the ranking algorithm. Bing followed suit with its own mobile-friendly algorithm.
2016– Google introduced “Possum” to combat local spam sites and integrated the Penguin update into its core ranking algorithm.
2017– Google penalized sites using intrusive interstitial and pop-up ads that negatively impacted the mobile user experience.
2018– Google introduced the BERT algorithm, a natural language processing model that significantly improved its understanding of search queries.
Google launched Google Search Console, a tool for website owners to monitor their site’s performance in search results.
2019 – Google implemented the Mobile-First Index, primarily indexing websites based on their mobile versions. Google Analytics 4 was launched, offering a more privacy-focused approach to web analytics.
2020– Google introduced Core Web Vitals, a set of metrics measuring website performance on mobile devices. Google My Business was launched to help businesses manage their online presence in Google Search and Maps.
2021– Google introduced the Multitask Unified Model (MUM), an AI model capable of understanding and responding to complex search queries. Google Search Highlights were introduced, providing snippets of information at the top of search results.
2022– Google rolled out the Page Experience update, incorporating Core Web Vitals as a ranking factor. Google Topics was launched, allowing users to search for information on specific topics.
White Hat vs Black Hat SEO
White-hat SEO refers to using only legitimate, search-engine-approved techniques to improve visibility in Google’s organic results. While black-hat SEO relies on prohibited or deceptive tactics (for example, cloaking, or buying links) to manipulate rankings and attract traffic. Another category sometimes used is grey hat SEO. This is in between the black hat and white hat approaches, where the methods employed avoid the site being penalized but do not act to produce the best content for users. Grey hat SEO is entirely focused on improving search engine rankings.

How SEO Tools Help In SEO?
Seo tools help in SEO in a lot of ways, e.g., they give us rough data to understand market conditions. The top SEO tools that are used are SEMrush & ahrefs. Many SEO tools on the market claim to filter out false or misleading content to drive more subscriptions, yet most SEOs end up repurposing those same tools for entirely different tasks. For more understanding, read the keyword difficulty myths.
How Many Seo Factors Or Techniques Are Needed to Rank In Google?
According to the google api leak, there are 14,000+ ranking factors or techniques that use Google to rank.
SEO Careers and Opportunities:
Demand for search-optimization talent keeps accelerating. LinkedIn’s most recent Workforce Report shows that marketing-related job postings (where “SEO” and “search marketing” are among the fastest-growing skill tags) rose 76 % year-over-year in early 2025, outpacing overall hiring across the platform.
A dedicated 2025 “State of SEO Jobs” study of 14,000+ listings paints an equally robust picture:
- 65 % of openings are now in-house roles versus 35 % at agencies.
- Mid-level positions dominate (59 %), with senior roles at 27 % and entry-level at 14 %.
- Work models are diversifying—34 % fully remote, 21 % hybrid, 45 % on-site—though the share of fully remote jobs has slipped slightly from its pandemic peak.
Role level | National-U.S. average pay | High-end share |
|---|---|---|
SEO Specialist | $84 795/yr (mean) | — |
SEO Specialist (broad sample) | $62 255/yr (median) | $122 720 max |
All senior SEO titles | — | 12 % of ads offer $100 000 + |
Is SEO, as Freelancing Is good?
Yes, working as a freelance SEO specialist is widely seen as a good move today. Research from Upwork shows freelancing is mainstream—64 million Americans earned money this way in 2023, four million more than the year before, and marketing skills like SEO are among the most-hired services. Pay is solid: Glassdoor pegs the average freelance SEO rate at about $33 per hour, SEO/SEM hybrids average $47, and Upwork’s own price guide puts most SEO experts between $15 and $35 with a median of $21.

Demand keeps climbing—U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics data predicts 8 % growth for marketing managers through 2033, faster than the national average—while platform data from SEMrush shows enterprise clients spent over $9 million on its SEO tools in 2024 alone, underscoring strong corporate budgets for search visibility.
Why choose an SEO internship instead of another digital marketing track?
An SEO internship gives you a 360-degree view of how technical performance, content strategy, UX, and analytics fit together. Skill demand keeps rising on 2025 “must-have” lists—so the role is a versatile launch pad for broader growth-marketing or product careers.
How To Choose an SEO Agency That Really Generates Results?
To choose seo agency, you define your goals & budget, then research agencies that have proof, real-time case studies, have the best communication, and read deeply their agency site to understand their methodologies of working. Upleadseo is the best option for you! It is very unique from others
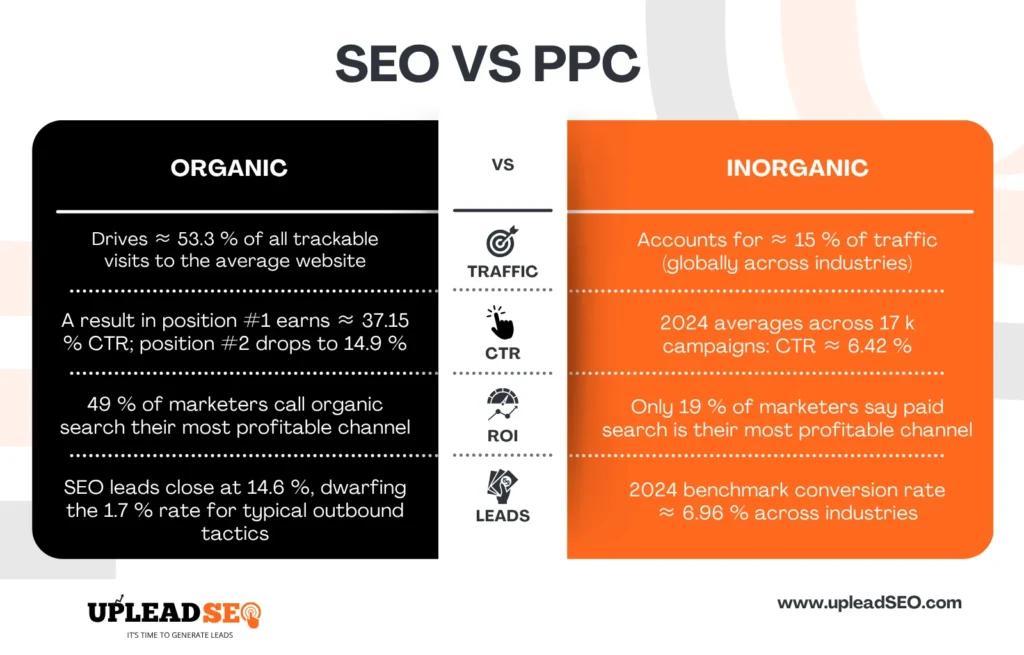
What Is The Difference Between Seo vs SEM?
SEO (search engine optimization) and SEM (search engine marketing) are two different but closely related terms. Search engine marketing has two children: ‘s SEO & ppc, we do optimization. One is organic marketing, and the other is inorganic or paid marketing, where we use ads to do marketing.
Dimension | SEO (Organic Search Optimization) | SEM (Paid Search/Google Ads) |
|---|---|---|
Share of web traffic | Drives ≈ 53.3 % of all trackable visits to the average website | Accounts for ≈ 15 % of traffic (globally across industries) |
Typical click-through performance | A result in position #1 earns ≈ 37.15 % CTR; position #2 drops to 14.9 % | 2024 averages across 17 k campaigns: CTR ≈ 6.42 % |
Cost & pricing model | No per-click fee; inbound/SEO leads cost 62 % less than outbound channels | Pay-per-click; 2024 averages: CPC $4.66 and cost per lead $66.69 |
Speed to results | Long ramp-up: only 1.74 % of brand-new pages reach Google’s top 10 within a year; the average #1 page is 5 years old | Immediate visibility as soon as the campaign is switched on; performance data within hours (no comparable lag reported in benchmark studies) |
Lead/conversion quality | SEO leads close at 14.6 %, dwarfing the 1.7 % rate for typical outbound tactics | 2024 benchmark conversion rate ≈ 6.96 % across industries |
User trust & behaviour | Users prefer organic results; 94 % of searchers say they skip paid ads, so organic listings capture the trust clicks first. | Must overcome ad-avoidance: the same study shows 94 % of users ignore paid listings—a built-in friction point. |
Marketer-perceived ROI | 49 % of marketers call organic search their most profitable channel. | Only 19 % of marketers say paid search is their most profitable channel |
PPC Vs Digital Marketing:
PPC is your fast-acting “paid tap” — you can open it today and water flows almost immediately, but every drop is metered. Broader digital marketing (SEO, content, email, social, etc.) is more like building an irrigation system — slow, labor-heavy up-front, yet dramatically cheaper (and often more abundant) once it’s running.
Key dimension | PPC (Pay-Per-Click) | Wider digital / inbound (organic, email, content, etc.) |
|---|---|---|
Speed to impact | Ads normally clear Google’s review in ≤ 1 business day and can start showing clicks the same day | Only 1.74 % of newly published pages reach Google’s top-10 within 12 months; the average page holding #1 is ~5 years old |
Typical click-through rate | Avg. Google Search Ads CTR 6.42 % across industries (2024) | First organic result earns 27.6 % CTR on average (2025 study) |
Traffic cost | Avg. cost-per-click $4.66 and cost-per-lead $66.69 in 2024 benchmarks | Inbound/content leads cost ≈ 62 % less than outbound and content itself costs 62 % less than traditional ads while generating 3× more leads |
Conversion rate | Avg. Google Ads conversion rate 7.52 % (2025) | Median landing-page conversion across industries 6.6 % — but pages reached via email convert 19.3 % on average |
ROI efficiency | Average Google Ads ROAS ~200 % (about $2 revenue per $1 spend) | Email returns $36 for every $1 invested; content marketing delivers compounding traffic at far lower marginal cost |
Use PPC when you need instant, controllable traffic and can afford the premium; invest in organic channels to drive down long-term acquisition costs and build durable equity. The sweet spot for most brands is orchestrating both: let PPC validate keywords and drive short-term pipeline while organic and email programmers accumulate authority and ROI over time.
SEO is not an appropriate strategy for every website, and other Internet marketing strategies can be more effective, such as paid advertising through pay-per-click (PPC) campaigns, depending on the site’s business goals.
How do I learn Seo In 2025?
Upleadseo is a deep knowledge base for the SEO readers or learners. UpleadSEO’s blog is packed with bite-sized tips, hands-on guides, and real-world examples. This is an encyclopedia of SEO information. Check our blog section to explore further Concepts and methodologies that others don’t describe.

